[Expression of connective tissue growth factor in sciatic nerve after chronic compression injury and effect of rhodiola sachalinensis on its expression].
Schlüsselwörter
Abstrakt
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the expression of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in the chronic sciatic nerve compression injury and to explore the effect of rhodiola sachalinensis on the expression of CTGF.
METHODS
Forty-five adult male Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into groups A, B, and C: In group A (sham-operated group), only the sciatic nerve was exposed; in group B (compression group), sciatic nerve entrapment operation was performed on the right hind leg according to Mackinnon method to establish the chronic sciatic nerve compression model; and in group C (compression and rhodiola sachalinensis group), the sciatic nerve entrapment operation was performed on the right hind leg and rhodiola sachalinensis (2 g/mL) was given by gavage at a dose of 0.5 mL/100 g for 2 weeks. The nerve function index (SFI) was observed and neural electrophysiology was performed; histology, transmission electron microscope, real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR, and Western blot were performed to observe the morphological changes of the compressed nerve tissue and to determine the mRNA and protein levels of CTGF, collagen type I, and collagen type III at 2, 6, and 10 weeks after operation.
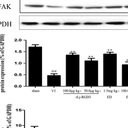
RESULTS
At 6 and 10 weeks after operation, SFI of groups A and C were significantly better than that of group B (P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference between groups A and C (P > 0.05). The nerve function test showed that the nerve motor conduction velocity (MCV) and the amplitude of compound muscle action potential (CMAP) of group B were significantly lower than those of groups A and C, and distal motor latency (DML) was significantly prolonged in group B (P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference between groups A and C (P > 0.05). Histology and transmission electron microscope observations showed that myelinated nerve fibers degenerated and collagen fiber hyperplasia after sciatic nerve chronic injury in group B, and rhodiola sachalinensis could promote the repair of nerve fibers in group C. At 2 weeks postoperatively, the number of myelinated nerve fibers in groups B and C were significantly less than that of group A (P < 0.05), and the myelin sheath thickness of groups B and C were significantly larger than that of group A (P < 0.05). At 6 and 10 weeks postoperatively, the number of myelinated nerve fibers in groups B and C were significantly more than that of group A (P < 0.05); the myelin sheath thickness of group B was significantly less than that of groups A and C (P < 0.05). The effective area of nerve fiber had no significant difference among groups at each time point (P > 0.05). Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR and Western blot results showed that the mRNA and protein expressions of CTGF, collagen type I, and collagen type III in group B were significantly higher than those in groups A and C at each time point (P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference between groups A and C (P > 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Sciatic nerve fibrosis can be caused by chronic nerve compression. The increased expression of CTGF suggests that CTGF plays an important role in the process of neural injury and fibrosis. Rhodiola sachalinensis can significantly reduce the level of CTGF and plays an important role in nerve functional recovery.