The teratogenicity and the action mechanism of gallic acid relating with brain and cervical muscles.
Λέξεις-κλειδιά
Αφηρημένη
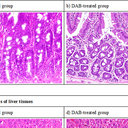
Gallic acid (3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) (GA) and other flavanoids are extensively used in nutraceuticals because of their antioxidant and antiinflammatory properties. While examining whether GA is effective in alleviating valproic-acid-induced teratogenesis in a chicken embryo model (CEM), we observed embryo hemorrhage and liposis in the musculi longissimus cervicis. We conducted this study to determine whether GA is inherently teratogenic and the extent to which the risk can be transferred to fetuses. A CEM was used to administer GA at 2, 6, 10, and 14 μM. GA at 2 μM did not exhibit cytotoxicity. At 6, 10, and 14 μM, GA caused severe decreases in body and liver weights, causing -5.6%, -21.3%, and -27.5% body weights and 4.0, 3.8, and 3.2-g, liver weights, respectively, in day-1 chicks. The optimal alive birth rate (or damaging rate) reached 33.3%, 39.4%, and 29.2% at 6, 10, and 14 μM GA, respectively. The damaged tissue was primarily cervical muscle (musculi longissimus cervicis), as evidenced by liposis, Zenker's necrosis, and hemolysis. The erythrocyte, hemoglobin, eosinophil, lymphocyte, and monocyte counts were severely reduced and PPAR-α was downregulated, whereas the Ras/Raf/JAK/STAT pathway was upregulated. The GA dose required to induce teratogenesis was ≥ 6 μM (1.02 mg/kg), which can be easily consumed by pregnant women in typical teas such as Chinese Pu-'Er and Chinese black teas, indicating a potential risk to human fetuses. GA at doses ≥ 1.02 mg/kg of body weight potentially causes characteristic cerebral hemolysis and liposis in the musculi longissimus cervicis. The mechanism of action of GA is multidisciplinary: The liposis can be ascribed to downregulation of PPAR-α; the erythrocyte hemolysis can be attributed to its unique autooxidative and prooxidant behavior and the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase; and the proliferation and differentiation deficits can be attributed to the upregulation of the Ras/Raf/JAK/STAT pathway.