S-nitrosoglutathione inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase upregulation by redox posttranslational modification in experimental diabetic retinopathy.
Słowa kluczowe
Abstrakcyjny
OBJECTIVE
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is associated with nitrosative stress. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the beneficial effects of S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) eye drop treatment on an experimental model of DR.
METHODS
Diabetes (DM) was induced in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Treated animals received GSNO eye drop (900 nM or 10 μM) twice daily in both eyes for 20 days. The mechanisms of GSNO effects were evaluated in human RPE cell line (ARPE-19).
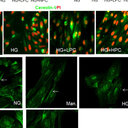
RESULTS
In animals with DM, GSNO decreased inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression and prevented tyrosine nitration formation, ameliorating glial dysfunction measured with glial fibrillary acidic protein, resulting in improved retinal function. In contrast, in nondiabetic animals, GSNO induced oxidative/nitrosative stress in tissue resulting in impaired retinal function. Nitrosative stress was present markedly in the RPE layer accompanied by c-wave dysfunction. In vitro study showed that treatment with GSNO under high glucose condition counteracted nitrosative stress due to iNOS downregulation by S-glutathionylation, and not by prevention of decreased GSNO and reduced glutathione levels. This posttranslational modification probably was promoted by the release of oxidized glutathione through GSNO denitrosylation via GSNO-R. In contrast, in the normal glucose condition, GSNO treatment promoted nitrosative stress by NO formation.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, a new therapeutic modality (GSNO eye drop) targeting nitrosative stress by redox posttranslational modification of iNOS was efficient against early damage in the retina due to experimental DR. The present work showed the potential clinical implications of balancing the S-nitrosoglutathione/glutathione system in treating DR.